Activity 2
Week 4
by GEORGETTE E. ZALDIVAR
Your patient recently had a viral infection and now she cannot move the muscles on the right side of her face. In addition, she is experiencing a loss of taste and dry mouth and she cannot close her right eye. Which cranial nerves have been affected by the viral infection?
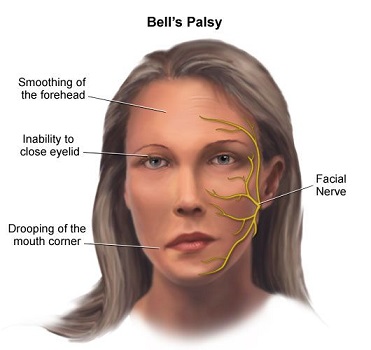
The patient’s symptoms from suffering a viral infection—such as the inability to move right facial muscles, loss of taste, dry mouth, and the inability to close her right eye—denote that the patient is suffering from a motor and sensory dysfunction in the seventh (VII) cranial nerve, otherwise known as the facial nerve. Damage to the said nerve can make it difficult for a person to blink, speak, eat, or convey emotions through facial expressions. The facial nerve's innervation of the orbicularis oculi muscles and the facial muscles can be used to explain why the right eye cannot be closed and why the right side of the face cannot move. In contrast, injury to the taste buds on the anterior region of the tongue, which creates the sensory axons for the facial nerve, is responsible for the lack of taste and dry mouth.
The clinical relationship between such symptoms suggests that the patient is suffering from the condition called Bell’s palsy, or idiopathic facial palsy, which is a condition that causes sudden weakness in the muscles on one side of the face.
References:
Tortora, G. J., & Derrickson, B. (2017). Principles of Anatomy & Physiology. Fifteenth edition; Wiley Loose-Leaf Print Companion. Hoboken, New Jersey, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.