Problem Set 8: Bioenergetics and Carb Catabolism
General Instructions
- This is a group activity.
- Answer the problems found below.
- Submit your answers in pdf/jpg formats only following the naming, Chem40_PS8_<Section>_<Group No.>
- Only one submission per group is needed.
Problems
1.Determine whether the following reactions will proceed favorably or spontaneously.
A. fructose-6-phosphate + ATP → fructose-1,6-diphosphate
B. glycerol phosphate + ADP → glycerol + ATP
C. phosphocreatine + ADP → creatine + ATP
2. Explain why the hydrolysis of the following compounds releases energy.
A. phosphoenol pyruvate
B. 1,3-diphosphoglycerate
C. succinyl CoA
3.The following are electron carriers in a hypothetical biological system. Give the arrangement of these carriers.
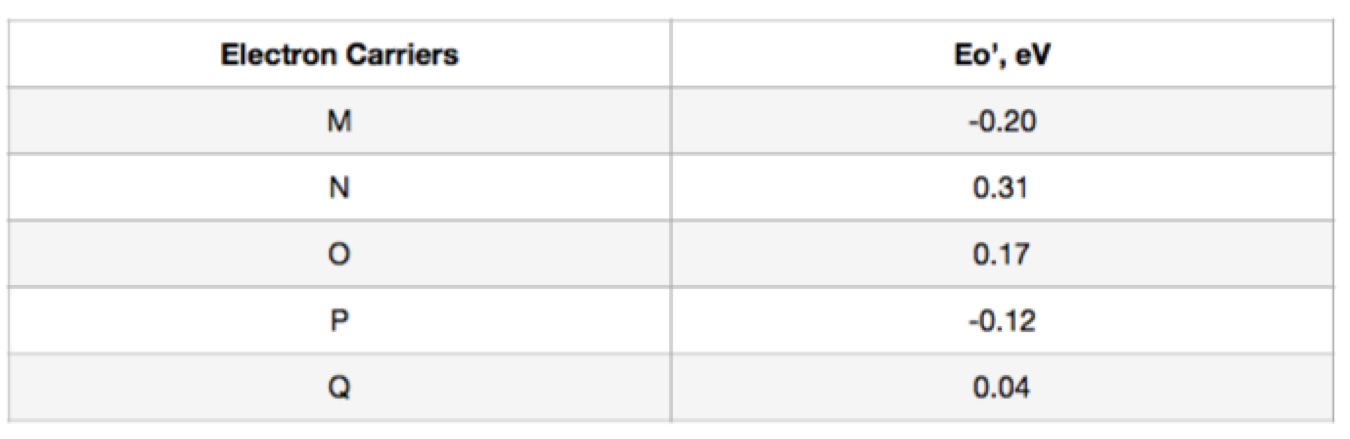
4. Why is the amount of ATP produced in cells that can undergo oxidative phosphorylation much greater than those that undergo substrate level phosphorylation only?
5. A boy was born with a mutation that causes his cells to not have the ability to produce the NADH dehydrogenase complex, the complex that allows the electron transport chain to make ATP from NADH. Will this patient be able to produce any energy at all from the ETC?
6. The drug, dinitrophenol (DNP), destroys the H+ gradient that forms in the electron transport chain. What is the most likely consequence?
7. How many ATPs can be produced from the oxidation of one molecule each of NADH and FADH2 in the electron transport chain in the presence of the following inhibitors:
A.Amytal B.Antimycin
8.Explain the toxicity of cyanide (CN-) and carbon monoxide (CO).
9.How many acetyl CoA(s) can be produced from the following?
a. Pyruvate
b. Succinate
c. Glycerol (think of an intermediate you will find in the glycerol-phosphate shuttle)
d. Fructose-1,6-diP
e. Sucrose
f.Sucrose from individual with defective triose phosphate isomerase
10.How many ATP units can be produced from the complete oxidation of the molecules in the previous problem (#9)?
11.Identify the committed step in each of the following pathways:
a. Glycolysis b. Glycogenolysis c.TCA cycle
12.In which of the following tissues/cells is glucose absorption dependent on insulin?
a. Liver b. Brain c.Kidneys d.Adipose tissue e.Erythrocytes
13. What is the implication of number 12 in the function of the tissues indicated?
14.A boy has an impairment in the enzyme, pyruvate dehydrogenase. What will be the amount of energy that can be produced in the oxidation of dextrin, a trisaccharide in the liver of this boy?