Course Guide
| Site: | UP Manila Virtual Learning Environment |
| Course: | Chemistry 40: Elementary Biochemistry |
| Book: | Course Guide |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Monday, 23 February 2026, 3:15 PM |
Description
This contains the topics and goals of the course. Parts of the course guide can also be downloaded here.
1. Course Description and Learning Outcomes
COURSE DESCRIPTION
This is a three-unit lecture course that focuses on the structure and function of biomolecular compounds: proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids and their roles in energy transduction and metabolism.
COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES
After completing the course, you should be able to:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the fundamental concepts in biochemistry.
- Discuss the reaction pathways involving biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids.
- Apply biochemical reaction pathways in the analysis of problems and situations accompanied by erroneous metabolism.
- Solve common qualitative and quantitative problems in biochemistry
OER TEXTBOOKS
You can download the following Open Education Resources as your reference for this course.
MAIN TEXTBOOK REFERENCES
Ahern, K., Rajagopal, I. (2015). Biochemistry: Free and Easy. Available at: https://biochem.oregonstate.edu/files/biochem/ahern/BiochemistryFreeandEasy3.pdf.
Ahern, K., Rajagopal, I., Tan, T. (2018). Biochemistry: Free For All. Available at: https://open.umn.edu/opentextbooks/textbooks/biochemistry-free-for-all-ahern.
Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Morgan, D., Raff, M., Roberts, K., Walter, P., (2015). Molecular Biology of the Cell, 6th Ed. New York: Garland Science.
Berg, J., Tymoczko, J., Stryer, L., Gatto, G. (2012). Biochemistry, 7th Ed. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.
Campbell, M., Farrell, S., & McDougal, O. (2017). Biochemistry. Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks Cole.
Nelson, D., Cox, M. (2008). Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 5th Ed. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.
Voet, D., Voet, J. (2011). Biochemistry, 4th Ed. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Copyright Notice
In compliance with intellectual property and fair use policies, no part of the materials here can be sold, distributed, or reproduced. Please note that permissions from attributed sources only allow the use of the materials within this class. Hence, uploading of class materials on sites like CourseHero etc. or sharing copies outside this class count as violations against the intellectual property rights of the attributed authors.
2. Course Outline
INTRODUCTION: The Sense of Biochemistry
BUFFERS AND LIVING SYSTEMS: pH, pKa, Ka, titration curves, Henderson-Hasselbach
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BIOMOLECULES
- Proteins
- Function of proteins
- Structure: 1°, 2°, 3°, 4°, pI
- Isolation and characterization methods
- Electrophoresis
- Chromatography
- Sequencing
- Others
- Enzymes
- Classification
- Kinetics: Km, Vmax, Michaelis-Menten, Lineweaver-Burke
- Minerals and coenzymes
Departmental Exam 1
2. Nucleic Acids
- Function
- Structure: 1°, 2° (A, B, Z), 3° (supercoiling), histones, chromatin
- Central dogma of molecular biology (Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes)
- Replication
- Transcription
- Post-transcriptional modifications
- Translation
- Post-translational modifications
- Mutation
- Types of mutation
- Effects of physical, chemical and viral agents on the structure and function of nucleic acids
- Protective mechanism and repair systems
- Isolation and Characterization methods
- Electrophoresis
- Polymerase chain reaction
- Recombinant DNA technology
- cDNA libraries
- Sequencing
- Others
Departmental Exam 2
3. Carbohydrates
- Structure and properties of carbohydrates
- Classifications and examples
- Chemical properties
- Physical properties
- Storage
- Structural
- Glycoproteins and proteoglycans
- Structure and properties of carbohydrates
4. Lipids
- Structure and properties of lipids
- Simple neutral lipids
- Phospholipids
- Compound lipids
- Components
- Organization
- Function and Transport Processes
- Structure and properties of lipids
METABOLISM
- Introduction: Design, Phases, Stages and Regulation
2. Bioenergetics
- Free energy, high energy compounds and coupled reactions
- Substrate level phosphorylation, electron transport chain, oxidative phosphorylation
- Inhibitors of ATP production
3. Catabolic Pathways and Metabolism
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Glycolysis
- Kreb’s cycle
- Glycogenolysis
- Lipolysis
- B – oxidation of fatty acids
- Transamination, oxidative deamination, direct deamination
- Metabolic fate of the carbon skeleton
- Metabolic fate of nitrogen
- Carbohydrate metabolism
Departmental Exam 3
- Anabolic Pathways and Regulation
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Gluconeogenesis
- Pentose phosphate pathway
- Biosynthesis of polysaccharides
- Lipid metabolism
- Biosynthesis of fatty acids
- Lipogenesis
- Ketogenesis
- Biosynthesis of cholesterol
- Nitrogen metabolism
- Biosynthesis of non essential amino acids
- Utilization of amino acids as precursors of non-protein compounds
- Nitrogen balance
- Metabolic pathways of purine and pyrimidines
- De novo synthesis
- Salvage pathways
- Carbohydrate metabolism
INTEGRATION OF METABOLISM
- Digestion and Absorption
- Transport Processes of Biomolecules in the Blood
- Role of Hormones and other Mediators in Metabolism
- Post Absorption and Starvation
Departmental Exam 4
3. Weekly Schedule
The table below shows in which weeks and sessions specific modules will be taken up.
|
Week No. |
Topic |
Topic Outcome |
Time Frame (hr) |
Learning Activities |
Learning Resources |
|
1 |
Orientation
Introduction to Biochemistry
Buffers - Definition of acid, bases, pH, pKa - Henderson-Hasselbalch equation - Titration curves |
- Relate biochemistry to the life sciences, particularly of biology and medicine
- Explain how buffers work in biological systems
- Solve problems on buffers
|
1.0
0.5
|
Synchronous through Zoom or other online meeting platform
Watch video/ Read module
Problem solving exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks
|
|
Amino Acids and pI |
- Explain the physiological and chemical properties of amino acids especially their function as biological buffers - Classify the amino acids according to their structures and properties |
1.5 |
Watch video/ read module
Solve problems and exercises |
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
2 |
Proteins: Structure and Function - Peptide bond - Levels of protein organization (collagen, hemoglobin) - Functions (catalytic, immunological, structural, etc.) |
- Explain how the nature of amino acids affect protein structure - Discuss the different functions of proteins in relation to their structures
|
1.5 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises |
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
Proteins: Isolation and Characterization Techniques |
- Differentiate techniques in isolating and purifying proteins and their applications
|
1.5
|
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
3 |
Proteins: Enzymes - Classification - Kinetics (Michaelis-Menten, Lineweaver-Burk) - Inhibition (irreversible, competitive, noncompetitive, uncompetitive)
|
- Discuss the concepts of enzyme catalysis - Differentiate types of inhibitors on enzyme catalysis - Solve problems involving enzyme kinetics
|
1.5
|
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks
|
|
- Factors affecting kinetics - Minerals, coenzymes, cofactors - Multienzyme complexes (pingpong, ordered, random, sequential) |
- Differentiate enzyme and multi-enzyme complexes |
1.5
|
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
4 |
FIRST EXAM |
||||
|
Nucleic Acids: Structure, Properties and Function - Central dogma - RNA vs. DNA - Levels of structural organization |
- Identify the components of nucleic acids - Explain the structural differences between DNA and RNA - Describe DNA structure and how it is packed in the cell |
1.5 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
Nucleic Acids: Replication of Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes |
- Describe how a new copy of DNA is synthesized |
1.5 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
5 |
Nucleic Acids: Transcription and Post-transcriptional modification |
- Describe how RNA is synthesized from DNA - Differentiate transcription in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes - Discuss post-transcriptional modifications in eukaryotes |
1.5 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
Nucleic Acids: Translation in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
Exceptions to the central dogma - Retroviruses and reverse transcription - Epigenetics |
- Describe how protein is synthesized from mRNA - Differentiate the mechanisms of translation in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
- Explain how retroviruses utilize their genetic material
- Differentiate epigenetic and genetic effects on gene expression |
1.0
0.5 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
6 |
Nucleic Acids: Mutations and Repair - Types of mutations - Effects of physical, chemical, and viral agents - Protective and repair mechanisms |
- Assess the different mechanisms of mutation and how various agents of mutation exhibit their effects on the structure and function of nucleic acids - Explain the various protective mechanisms and repair systems in cells |
1.5 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
Look into: Chem 41\BRCA-1scenario.pdf
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
Nucleic Acids: Isolation, characterization and manipulation methods - Basic recombinant DNA techniques - Current approaches to DNA manipulation and analysis |
- Explain the techniques used in recombinant DNA technology - Discuss current approaches to DNA manipulation and analysis
|
1.5
|
Watch video/ Read module
Answer discussion questions |
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
7 |
SECOND EXAM |
||||
|
Carbohydrates: Structure and Function |
- Relate the structures, properties, and reactivities to the functions of carbohydrates - Draw carbohydrate structures |
1.5 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
Carbohydrates: Functions of polysaccharides |
- Differentiate the structure and function of polysaccharides |
1.5
|
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
8 |
Lipids: Structure and Function |
- Relate the structures and properties to the functions of lipids - Draw lipid structures - |
1.5
|
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
Biological Membranes and Membrane Transport |
- Relate membrane structure to its functions - Discuss transport mechanisms in membranes
|
1.5
|
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
9 |
Bioenergetics - Introduction to metabolism, stages, and regulation - Free energy, high energy compounds, and coupled reactions - Substrate level phosphorylation - Oxidative phosphorylation - Electron transport chain - Inhibitors of ATP chain - Other energy transducing reactions |
- Present an overview of metabolism - Apply the laws of thermodynamics in the maintenance of cellular functions - Discuss the methods of ATP synthesis and processes that affect it - Enumerate important biological reactions that use and produce energy |
1.5 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks
|
|
Carbohydrate Catabolism - Glycolysis - Kreb’s cycle - Glycogenolysis - Anaerobic respiration (ethanol fermentation, lactic acid fermentation) |
- Discuss cellular respiration as the major catabolic and energy-producing pathway of all cells - Illustrate various catabolic pathways for carbohydrates |
1.5
|
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
10 |
Continuing on Carbohydrate Catabolism |
|
1.5 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises |
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks - |
|
Lipid Catabolism - Lipolysis - β-oxidation |
- Discuss the role of lipids as alternative sources of energy and the different reactions in the |
1.0 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
11 |
Amino Acid Catabolism - Transamination, oxidative deamination, direct deamination - Amino acid catabolism - Nitrogenous base catabolism - Urea cycle
Nucleic Acid Catabolism - Purine and Pyrimidine Catabolism |
- Discuss the role of amino acids as primary or alternative sources of energy - Trace the fates of the amino group and carbon skeleton of amino acids - Calculate and compare the ATP generated from various sources
- Explain nucleic acid catabolism |
2.0 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
THIRD EXAM |
|||||
|
Carbohydrate Anabolism - Gluconeogenesis - Glycogenesis and regulatory enzymes - Pentose phosphate pathway |
- Discuss the pathways leading to the synthesis of glucans and glucose |
1.5 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
12 |
Lipid Anabolism - Biosynthesis of fatty acids - Lipogenesis - Ketogenesis - Biosynthesis of cholesterol and eicosanoids - Lipid transport: HDL, LDL, VLDL, chylomicrons |
- Present the pathways that cells undergo in order to synthesize fatty acids - Discuss the pathways that liver cells undergo to compensate for the decrease in dietary sources of energy - Explain the reactions leading to cholesterol synthesis and how these processes are regulated |
1.5 |
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
Nitrogen Anabolism - Biosynthesis of amino acids - De novo and salvage pathways of nitrogenous bases |
- Summarize the precursors and pathways leading to the synthesis of amino acids and nucleotides |
1.5
|
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
13 |
Integration - Digestion and Absorption of Foodstuffs - Metabolic Patterns in Animals (e.g. plasma levels of glucose, fatty acids and ketone bodies) - Integration and Regulation of Metabolic Pathways |
- Correlate the various metabolic pathways - Compare the levels of metabolites during the different stages of metabolism - Differentiate metabolic needs of various organ systems - Discuss how various metabolic pathways are regulated |
3.0
|
Watch video/ Read module
Solve problems and exercises
|
- Online Videos/ References - Lectures - Modules - Textbooks |
|
|
FOURTH EXAM |
||||
|
14 |
FINAL EXAM |
||||
You can also download this table here.
4. Mode of Delivery
For this Second Semester, AY 2020-2021, the course is delivered using our university’s learning management system (LMS), the UP Manila Virtual Learning Environment (VLE). The course is designed to enable independent and self-paced study among the learners through the posting of all the topics and important references that will serve as guide.
Asynchronous Sessions (required): Content will largely be delivered asynchronously meaning they can be accessed outside of the indicated SAIS class hours. Recorded lecture videos or live sessions, readings, and tasks will be uploaded. Materials on LMS as well as specific rubrics in activities will also serve as guide in the completion of requirements.
Synchronous Sessions (not required): Synchronous sessions will happen during our class hours which will also serve as our scheduled online consultation if you have any questions about the coverage.
5. Course Requirements
PRE-FINAL CLASS STANDING (2/3)
- Four (4) Departmental Exams (60%)
- Class activities (20%)
- Class quizzes and probsets (20%)
FINAL EXAM (1/3)
Grading System
% Grade Eq.
[90, 100] 1.00
[85, 90) 1.25
[80, 85) 1.50
[75, 80) 1.75
[70, 75) 2.00
[65, 70) 2.25
[60, 65) 2.50
[55, 60) 2.75
[50, 55) 3.00
[40, 50) 4.00
[0, 40) 5.00
6. Course Policies
By proceeding with this online class, you agree to the Code of Honor below:
"I will work on the activities on my own without the help of another person, unless said so by the instructor. I will not share course materials made available in the LMS to those who are not enrolled in this subject. I will not make solutions to homework and exams available in any way to other learners. I will not engage in any other activities that will dishonestly improve my results or dishonestly improve or damage the work of others."
(edited and adopted from https://mooc.house/)
- Submit and comply with all course requirements.
- Actively participate in group work and discussions through the given LMS platform or through synchronous sessions.
- Politely and respectfully interact with instructors and classmates in all remote platforms.
- Must take ALL exams (including final exam if required).
- Criterion for finals exemption: MUST PASS all departmental exam (at least 50%).
- All forms of cheating will NOT BE TOLERATED and will merit a grade of 5.0. (Students will not be allowed to drop the course if found guilty.)
7. Guide for the Synchronous Sessions
Pre-session:
- Install an application for viewing PDF files
- Check that your phone/desktop is fully charged.
- Check that you have your charger, headsets, and other necessary equipment that you might use during our Synchronous sessions
- Log-in a few minutes early so you can check your audio and/or video prior to the start of the online session
During:
- Use your UP Mail in joining Zoom/Google (or other online platform) meetings
- Mute your microphone when you enter the room.
- Use icons to express yourself ("clap", "thumbs up" etc.). You may use the “Raise Hand” icon you want to speak (available in Zoom).
- Contact (Email or SMS) the instructor/classmate when you are having connectivity issues.
Post-session:
- Use the designated VLE forum or messaging for questions and concerns, so that the entire class can participate in them as well.
You will be receiving meeting details through the Announcement or Calendar blocks. These should be seen either at your Course Page or the Dashboard.
8. Policies for Group Work, Submissions, Questions
Please practice ACADEMIC INTEGRITY AT ALL TIMES.
Group work
- Groups are assigned at random. Please get to know your group mates, group messaging is allowed so you can contact them through the VLE messaging platform:
(found in the upper right corner of your page).
- Please use the forums for discussions so that your interactions and contributions are documented. You are allowed to speak in whatever language that suits you, however, we would like to emphasize respect and disbar foul language.
- For Group submission, a single submission from a group member will suffice.
- You will be asked to rate your team members and their contributions to a group work. Please rate them objectively.
- To all members, please actively participate and contribute to your group. They are your accountability and study team in this remote education.
Individual Work
- All assignment submissions will be via the VLE platform unless otherwise indicated by the instructor.
- Please read and follow instructions carefully especially when submission types are specified.
- If multiple submissions are done, only the most recent submission will be checked.
- Take note of deadlines and try to follow them as much as you can. We will try to post activities ahead of time so that you can make contingency plans in the submissions like internet/gadget access.
Quizzes
- Please assume that this is a normal classroom quiz with closed notes and no other tabs or googling available unless stated otherwise.
- Please be ready with your gadgets and internet accessibility when taking quizzes especially the timed ones.
- Please let your instructor know right away when you have trouble accessing quizzes.
Forums/Discussions
- This is the main platform for class interactions and for posting of questions or clarifications.
- For class concerns, please put them here so that others who might have the same questions will be included and will also receive the answer. DO NOT INDIVIDUALLY MESSAGE the instructor for this. It will spam our emails/message boards and we might not be able to get to your question.
- Use this platform to simulate a normal class conversation. Again, no language specifics - formal or informal is fine - as long as we are respectful of each other.
For Clarifications/Questions/Concerns
- As stated, the main platform for posting these is through the forums.
- The main methods for contacting the instructors are through the forums and message boards.
- Email addresses or mobile numbers are secondary means of communication if the first two methods fail.
- Please give us 24-72 hrs to respond to your queries.
- Live consultations (synchronous sessions) will also be platforms to address questions accumulated throughout the week or for other discussions.
9. Meet your Instructor
|
|
CIARA CHRISTIANNE Y. LIMAssistant ProfessorSections: MHG, MHI1Email address: cylim1@up.edu.ph*Mobile No.: 09988833535**use IF URGENT |
|
Working hours: M-F 8:00 am-5:00pm Best time to ask questions regarding class is during the allotted class hours. Please use the messaging platform or the forum boards for your class questions to streamline class information. |
The Chem 40 Course Team |
|
 |
Dr. Ma. Constancia CarrilloMark Jeremiah CleofasCiara Christianne LimDr. Marcelina LirazanDr. Marilou Nicolas |
Happy Sem, kiddos!
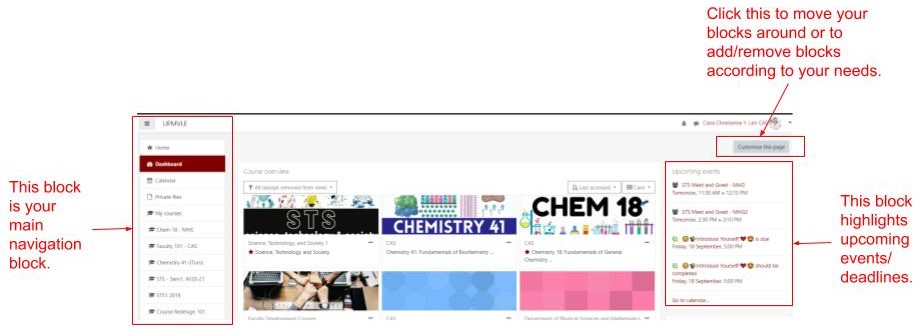
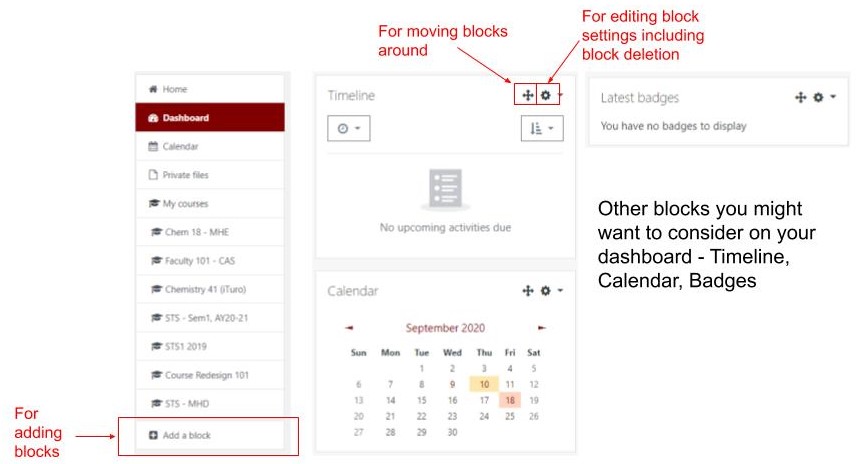
10. Explore the VLE platform
Get to know your learning platform and its features. Look around and see what you can do with it.
Here are some sites you can check out for this:
- https://docs.moodle.org/20/en/Student_tutorials
- http://45.55.1.62/images/currentStudents/eLearning/studentResources/studentQuickStartMoodleGuide.pdf
You can also download the Moodle mobile app on your phone/tablet and configure the VLE website (vle.upm.edu.ph) into it.
For your dashboard, here are some of the things you might want to look around on: